Describe the Effects of the Oceans on Weather and Climate
In fact says OGorman humidity rises about 35 for every degree Fahrenheit that the temperature rises. The changes in current movements affect the coastal climate by carrying a lot of heat.

Pin On A Very Basic Idea Of Global Warming And Its Prevention
Increased ocean acidity makes it more difficult for certain organisms such as corals and shellfish to build their skeletons and shells.

. Increasing wildfire insect outbreaks and tree diseases are causing widespread tree die-off. For example Europes relatively mild climate is maintained in part by the large Atlantic current called the Gulf Stream which is experiencing an unprecedented slowdown Changing these currents will have major. The ocean absorbs heat from the Sun and ocean currents move that warm water all around the planet.
During an El Niño event sea surface temperatures over the central and eastern Pacific become warmer than normal. The higher the humidity the harder it is for our bodies to cool off by sweating which can be uncomfortable but also increases health risks from exhaustion fainting and even life-threatening heat stroke. Sea level rise erosion inundation risks to infrastructure and increasing ocean acidity pose major threats.
Most of the rain that falls on landcomes from the tropical ocean. How does the ocean affect the climate. The circulation of the oceans is affected by variations in atmospheric circulation.
The ocean is the primary driver of weather and climate and can give us clues to global phenomenon such as El Niño. The oceans influence climate by absorbing solar radiation and releasing heat needed to drive the atmospheric circulation by releasing aerosols that influence cloud cover by emitting most of the water that. They affect one another primarily through the transfer of heat and moisture.
Although the oceans help reduce climate change by storing large amounts of carbon dioxide increasing levels of dissolved carbon are changing the chemistry of seawater and making it more acidic. Higher incidences of flooding can lead to the spread of waterborne diseases injuries and chemical hazards. The oceans play a critical role in storing heat.
Cold water near the North and South Poles sinks deeper into the ocean. Even with their vast capacity to absorb heat and carbon dioxide oceans were 017 degrees Celsius 03 degrees Fahrenheit warmer in 2017 than in 2000 and the warming trend appears to be accelerating. Ocean currents circulate the effects of temperature change slowly for great distances.
What are some of the signs of climate change. This great reservoir continuously exchanges heat moisture and carbon with the atmosphere driving our weather patterns and influencing the slow subtle changes in our climate. This would further block the formation of sea ice and disrupt the sinking of denser cold salty water.
If you have spent time at the beach or in a coastal city you will likely appreciate the way in which the ocean affects the weather and climate of the coastal region. This includes major long-term changes in temperature precipitation humidity ocean heat wind patterns sea level sea ice extent and other factors and how these changes affect life on Earth. Weather and climate are influenced by interactions involving sunlight the ocean the atmosphere ice landforms and living things.
Dry conditions lead to more wildfires which bring many health risks. Normally strong trade winds blow from the east along the equator ocean waters are warm and rainfall is plentiful over the western Pacific while over the central and eastern Pacific ocean waters are cool and conditions are dry. Understanding and predicting precipitation is critical to farmers who decide which crops to plant and how deep based in part on soil moisture levels.
Climate and the oceans The atmosphere and the oceans are intimately related. Warm ocean waters provide the energy to fuel storm systems that provide fresh water vital to all living things. In turn surface winds push against the surface of the ocean creating currents that help control the distribution of warm and cold waters.
The phytoplankton microscopic plants that live in the ocean are responsible for almost half the oxygen you inhale and play a vital role in the carbon cycle. Rising sea levels expose higher locations. In the summer the ocean acts to cool the land and in the winter the opposite effect occurs and the land is kept warmer.
Or local climate is its proximity to the oceans. Changes in the energy balance between the oceans and atmosphere play an important role in the planets climate change. Surface currents are driven by the force of the wind pushing on the ocean surface.
Sea level rise poses widespread and continuing threats to the regions economy and environment. The movement of the ocean water is caused by forces acting on the water including the breaking waves salinity differences Coriolis effects the wind temperatures and cabbeling. These interactions vary with latitude altitude and local and regional geography all of which can affect oceanic and atmospheric flow patterns.
More heat in the atmosphere and warmer ocean surface temperatures can lead to increased wind speeds in tropical storms. Climate change results from both human activities and natural causes. The frictional drag of the wind on the surface layer of the.
Climate change is taking a toll on forests farms freshwater sources and the economy but ocean ecosystems remain the epicenter of global warming. As ocean temperatures rise hurricanes are getting stronger and wetter which can cause direct and indirect deaths. And warmer air can hold more water.
Climate change leading to increases in ocean temperatures evaporation of seawater and glacial and sea ice melting could create an influx of warm freshwater onto the ocean surface. Ocean currents are like highways that carry water around the world. The ocean emits some of its heat up into the atmosphere both in the form of thermal energy and water vapor creating winds and rain clouds.
When the earths surface cools or is heated by the sun the temperature change is greater - and faster - over the land than over the oceans. Ocean current is a directed permanent or continuous movement of oceans water. The ocean plays a central role in regulating the Earths climate.
Oceans have tremendously high heat capacity so they have a large damping effect on climate. As more water vapor is evaporated into the atmosphere it becomes fuel for more powerful storms to develop. The impacts of changes in ocean currents on humanity could be severe as currents play a major role in maintaining Earths climate.
The ocean plays an important role in shaping our climate and weather patterns. A 2013 assessment found that oceans had absorbed 93 of the excess heat generated by greenhouse gas emissions since 1970 contributing to the increased average global sea temperatures rising by about 013 degrees Celsius. Greenhouse gases act to reduce the amount of energy that is emitted back to space by Earth leaving more heat within the atmosphere land and in particular the oceans resulting in an imbalance as more energy from the sun.
At the front line of climate change the ocean the coastlines and coastal communities are being disproportionately impacted by increasing carbon dioxide CO 2 and other greenhouse gas GHG emissions from human activities. MS-ESS2-6 The ocean exerts a major influence on weather and. Heat along with salt is a major source of power for ocean currents.
Heat energy moves from the oceans to the atmosphere through the processes of direct heat transfer and evaporation and energy from the atmosphere flows to the oceans in the form of precipitation.

Air Temperature Near Surface Humidity Temperature Over Oceans Sea Surface Temperature S Global Warming Climate Change Climate Change Climate Change Effects

Ocean Pollution 6 Things That Make It Worse Ocean Pollution Ocean Marine Pollution

What Role Does The Ocean Play In The Weather

23 Children S Books To Inspire Ocean Conservation Picture Book Inspiration For Kids Childrens Activities

Check How Those Estimates Make Sense What Are The Likely Effects Of Global Warming On Those Figures Water Cycle Water Cycle Worksheet Global Warming

Stratospheric Winds Affect Ocean Circulation Sott Net Polar Vortex Earth And Space Science Weather And Climate

Global Climate Change Explorer Oceans And Water Exploratorium

Oceans Of The World Arctic Weather Weather And Climate Oceans Of The World

Sinking Beauty By Roy Park Age 14 Bow Seat Student Artist Perubahan Iklim Beruang Kutub Ilustrasi

Nasa S Climate Kids Home Weather And Climate Energy Solar Energy

What Role Does The Ocean Play In Weather

Map What Is The Thermohaline Circulation Circulation Ocean Earth Science

Effects Of Global Warming Climate Change Effects Global Warming

New Study Warns Of Dangerous Climate Change Risks To The Earth S Oceans Dana Nuccitelli Weather And Climate Oceans Of The World Climate Change
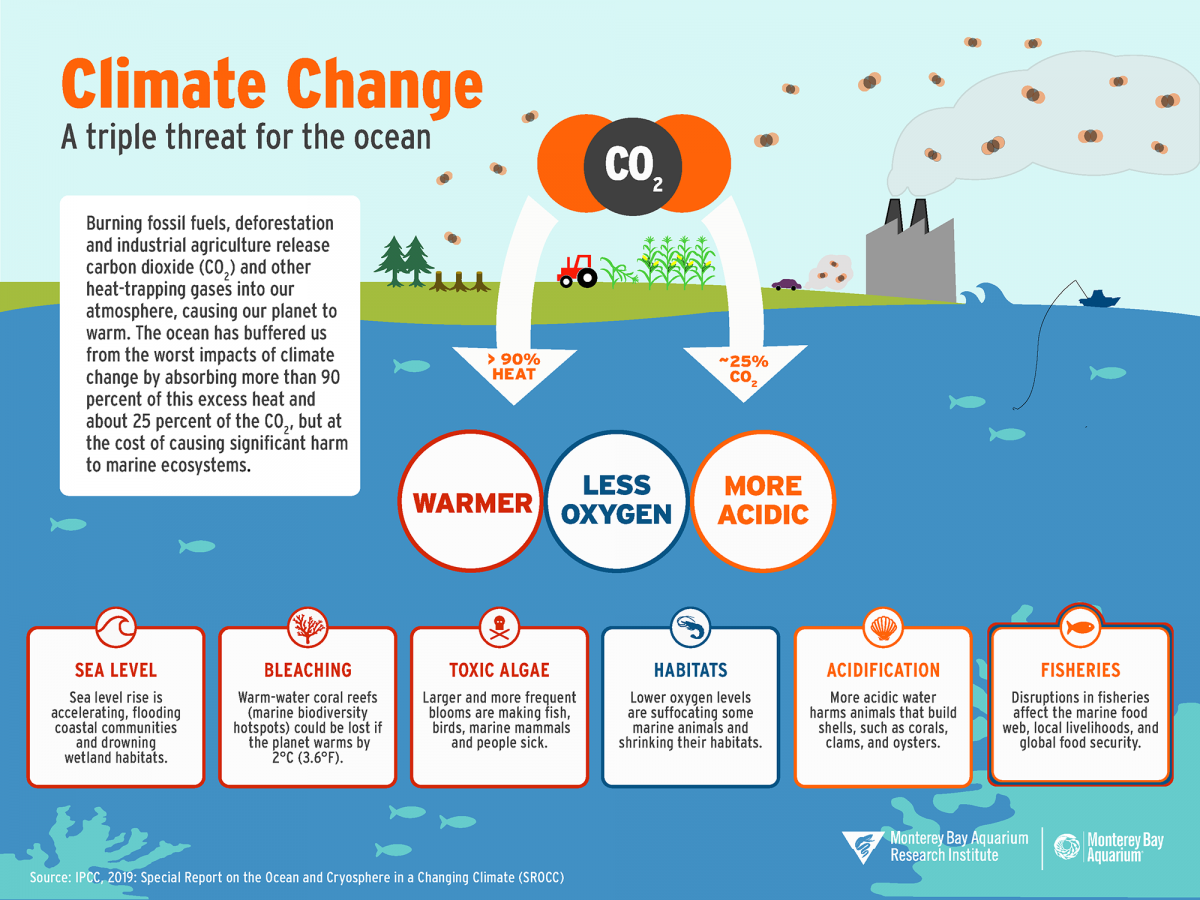
Climate Crisis And Ocean Warming The Shape Of Life The Story Of The Animal Kingdom

Twitter Ocean Acidification Climate Change Facts Ocean

What Are Climate Models And How Accurate Are They What Is Climate Weather And Climate Mathematics

A Major Ocean Current May Be Hurtling Towards Collapse Ocean Systems Major Oceans Parts Of The Earth

Climate Kids Review For Teachers Common Sense Education Climate Change Poster Climate Change Effects Climate Change
Comments
Post a Comment